Marketing refers to the process of identifying, anticipating, and satisfying customer needs and wants through the creation, promotion, distribution, and pricing of goods and services. The nature and scope of marketing are vast and complex, and it encompasses a wide range of activities, including market research, product development, branding, advertising, sales, customer service, and more.
The primary aim of marketing is to create value for both the business and its customers. It involves creating and maintaining a strong brand image, understanding customer preferences and behavior, and building strong relationships with customers. Marketing is not limited to selling products or services; it is a holistic approach that involves every aspect of the business.
As per AMA Marketing is the activity, set of institutions, & processes for creating, communicating, delivering, & exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society.
For example, let’s consider the marketing efforts of a company like Apple. Apple’s marketing strategy revolves around creating products that are not only high-quality but also innovative and aesthetically pleasing. The company invests heavily in product development and research to ensure that its products meet the changing needs of its customers.
Apple’s marketing also involves creating a strong brand identity through its advertising and promotional activities. Its “Think Different” campaign is one such example. The campaign was aimed at creating a sense of individuality and creativity among Apple’s customers, and it was highly successful in creating a loyal customer base for the company.
Moreover, Apple’s marketing efforts extend beyond just selling products. The company’s retail stores are designed to offer an immersive customer experience that reinforces the brand’s image and builds a strong relationship with its customers. The Apple Store Genius Bar is an excellent example of this approach, where customers can receive one-on-one technical support and advice, enhancing the overall customer experience.
Example: Amul is a dairy cooperative that produces a wide range of dairy products in India, including butter, milk, cheese, and more. Amul’s marketing strategy focuses on creating a strong brand image through its advertising campaigns, which often feature catchy slogans and memorable taglines, such as “Utterly Butterly Delicious” and “The Taste of India.”
Amul’s marketing efforts also involve creating a strong distribution network that reaches every corner of India, from rural villages to urban centers. This ensures that its products are easily accessible to consumers across the country, and it has helped Amul become one of India’s most trusted and recognizable brands.
Furthermore, Amul’s marketing efforts extend beyond just selling products. The company has also focused on creating a sense of social responsibility and community involvement through various initiatives, such as supporting farmers and providing employment opportunities for women.
Overall, Amul’s marketing strategy demonstrates the importance of creating a strong brand image, understanding customer preferences and behavior, and building strong relationships with customers. By doing so, Amul has been able to build a loyal customer base, become a household name in India, and achieve great success in the dairy industry.
NATURE OF MARKETING
The nature of marketing refers to the fundamental principles and activities that are involved in the creation, delivery, and exchange of value between a company and its customers. In general, marketing involves identifying customer needs and wants, developing products and services that satisfy those needs, promoting those products and services to target customers, and delivering them in a way that maximizes customer satisfaction.
Example: HUL is a subsidiary of the global consumer goods company, Unilever, and operates in India across a range of categories, including personal care, home care, and foods.
HUL exemplifies the nature of marketing through its customer-centric approach. The company places a strong emphasis on understanding the needs and preferences of its customers and developing products and services that meet those needs. For example, the company has developed a range of products under its “Dove” brand that are specifically designed for Indian women, taking into account their unique beauty needs and preferences.
In addition, HUL is also known for its innovative marketing strategies. The company has launched a number of successful marketing campaigns in India that have resonated with consumers and helped to build strong brand loyalty. For example, HUL’s “Swachh Aadat, Swachh Bharat” campaign, which promotes the importance of handwashing, has been widely praised for its effectiveness in changing consumer behavior.
Overall, HUL’s customer-centric approach and innovative marketing strategies illustrate the nature of marketing, which involves identifying customer needs, developing products and services that meet those needs, and promoting them in a way that resonates with target customers.
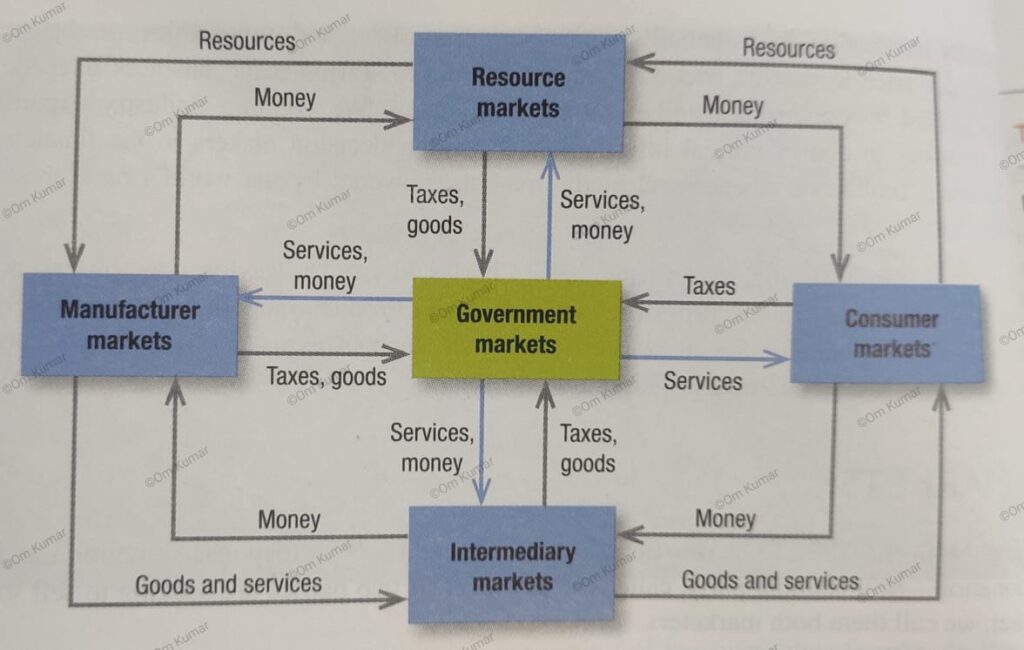
SCOPE OF MARKETING
The scope of marketing refers to the range of activities and functions that fall under the domain of marketing. The scope of marketing has expanded over the years and now includes a wide variety of activities that are aimed at creating, communicating & delivering value to customers.
CORE MARKETING CONCEPTS
- Needs, Wants & Demands
- Target Markets, Positioning & Segmentation
- Offerings & Brands
- Marketing Channels
- Paid, Owned & Earned Media
- Impressions & Engagement
- Value & Satisfaction
- Supply Chain
- Competition
- Marketing Environment
TRADITIONAL MARKETING
Traditional marketing refers to the use of traditional media channels, such as print, radio, and television, to promote a product or service. It is a type of outbound marketing where businesses push their messages out to a broad audience in the hopes of attracting potential customers.
Example: Hindustan Unilever Limited (HUL) brand, Lux Soap. Lux Soap has been using traditional marketing methods since the early 20th century and has successfully created a strong brand image over the years. The company has used print ads, billboards, and television commercials to promote its product, featuring Bollywood celebrities and their endorsements. By using these traditional marketing channels, Lux Soap has been able to reach a broad audience and increase brand recognition, making it one of the most popular soap brands in India.
Example: Indian Railways. The Indian Railways has been around for over 150 years and has relied on traditional marketing methods to attract customers. The company has used print ads, radio ads, and billboards to promote its services to the general public. In addition, the company has also used brochures and pamphlets to educate potential customers about its various services, routes, and fares. By using these traditional marketing channels, the Indian Railways has been able to attract a wide range of customers from different demographics, making it one of the most popular modes of transportation in India.
In conclusion, traditional marketing has been an effective way for Indian businesses to promote their products and services over the years. By using traditional media channels, businesses can reach a broad audience and increase brand recognition, making it an essential component of a comprehensive marketing strategy.
COMPONENTS OF TRADITIONAL MARKETING
- Print Advertising: This includes placing ads in newspapers, magazines, and trade publications. For example, Coca-Cola may place an ad in a magazine like Vogue to reach its target audience of fashion-conscious women.
- Broadcast/Electronic Advertising: This involves placing ads on television and radio. For example, a car manufacturer like Toyota might air a commercial during a popular TV show to reach a broad audience.
- Outdoor Advertising: This includes billboards, bus shelters, and other outdoor signage. For example, McDonald’s might place a billboard along a busy highway to reach a large number of drivers.
- Events and Promotions: This includes sponsoring events, such as concerts or sports events, and holding promotional activities, such as product demonstrations or contests. For example, Red Bull might sponsor an extreme sports event and hold a contest for attendees to win free product samples.
MODERN MARKETING
Modern marketing refers to the use of modern digital technologies, such as social media, search engines, and mobile devices, to promote a product or service. It is a type of inbound marketing where businesses attract potential customers through targeted and personalized content that is relevant to their interests and needs.
Example: Flipkart. Flipkart has been using modern marketing methods since its inception in 2007 and has revolutionized the e-commerce industry in India. The company has leveraged social media, search engine optimization, and mobile apps to reach customers and increase sales. Flipkart has been successful in building a loyal customer base through personalized recommendations and targeted advertisements based on customer search history and preferences. By using modern marketing channels, Flipkart has been able to create a seamless and convenient shopping experience for its customers, making it one of the most popular e-commerce platforms in India.
Example: Zomato, an online food ordering and delivery platform. Zomato has been successful in using social media platforms like Instagram and Twitter to engage with its customers and create a strong brand image. The company has leveraged user-generated content and influencer marketing to increase brand awareness and drive sales. In addition, Zomato has also used data analytics and personalized recommendations to offer customized food options to its customers. By using modern marketing channels, Zomato has been able to provide a seamless and convenient food ordering experience for its customers, making it one of the most popular food delivery platforms in India.
COMPONENTS OF MODERN MARKETING
Modern marketing incorporates digital technologies and platforms to reach consumers through various channels. The components of modern marketing include:
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): This involves optimizing a website’s content and structure to rank higher in search engine results. For example, a restaurant might optimize its website for keywords like “best punjabi restaurant in town” to rank higher in local search results.
- Social Media Marketing: This includes using social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter to engage with customers and promote products or services. For example, a clothing brand might use Instagram to showcase its latest collection and interact with customers through comments and direct messages.
- Content Marketing: This involves creating valuable and relevant content, such as blog posts, videos, and infographics, to attract and engage customers. For example, a financial services company might publish blog posts on personal finance tips and create videos on investment strategies to attract potential customers.
- Email Marketing: This includes sending targeted emails to subscribers with offers, promotions, and personalized content. For example, a beauty brand might send an email to its subscribers with a personalized skincare routine based on their skin type and concerns.
- Influencer Marketing: This involves collaborating with influencers, who have a large following on social media, to promote products or services. For example, a fitness brand might collaborate with a fitness influencer to promote its workout gear to their followers.
Overall, modern marketing has been an effective way for Indian businesses to promote their products and services in the digital age. By leveraging modern digital technologies, businesses can attract potential customers through targeted and personalized content that is relevant to their interests and needs, making it an essential component of a comprehensive marketing strategy.
MARKETING ENVIRONMENT
Marketing environment refers to the internal and external factors that affect a company’s ability to market its products or services effectively. These factors include economic, social, cultural, technological, legal, and political factors. Understanding the marketing environment is critical for businesses to develop effective marketing strategies that can adapt to changing market conditions and consumer behavior.
Example of marketing environment is the rise of e-commerce in India. E-commerce has revolutionized the way people shop and has disrupted the traditional brick-and-mortar retail industry. The rapid growth of e-commerce in India has been driven by several factors, including the increasing penetration of the internet and smartphones, the convenience of online shopping, and the availability of a wide range of products and services. This has created a highly competitive and dynamic marketing environment for businesses operating in the retail industry.
Another example of marketing environment in India is the impact of government policies on businesses. The Indian government has introduced several policies and regulations that affect the marketing activities of businesses, including tax policies, import-export regulations, and consumer protection laws. For instance, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) introduced in 2017 has had a significant impact on the pricing and distribution strategies of businesses in India.
Moreover, the changing social and cultural environment in India also affects marketing activities. For instance, the increasing awareness and concern about environmental issues have led to a growing demand for eco-friendly and sustainable products. Many businesses in India have responded to this trend by incorporating sustainable practices into their operations and marketing strategies.
FACTORS AFFECTING MARKETING ENVIRONMENT
Several internal and external factors can affect the marketing environment of a business. These factors can be broadly classified into the following categories:
- Economic Factors: Economic factors such as inflation, interest rates, consumer income, and purchasing power can have a significant impact on a business’s marketing environment.
- Social and Cultural Factors: Social and cultural factors such as demographics, consumer attitudes and beliefs, social trends, and cultural values can affect consumer behavior and preferences, which, in turn, can influence a business’s marketing strategy.
- Technological Factors: Technological factors such as innovation, research and development, and the adoption of new technologies can impact a business’s marketing environment. Technological advancements can create new opportunities for businesses to reach customers and offer new products and services.
- Political and Legal Factors: Political and legal factors such as government policies and regulations, trade agreements, and taxation can impact a business’s marketing environment. For instance, changes in tax policies or import/export regulations can affect a business’s pricing and distribution strategies.
- Competitive Factors: Competitive factors such as the number and strength of competitors, market share, and market trends can impact a business’s marketing environment. The competitive landscape can influence a business’s marketing strategy, pricing, and distribution decisions.
In conclusion, understanding the various factors that affect the marketing environment is critical for businesses to develop effective marketing strategies that can adapt to changing market conditions and consumer behavior. By analyzing these factors, businesses can identify opportunities and challenges and develop marketing plans that maximize their chances of success in the market.
MARKETING V/S SELLING
Marketing and selling are two different concepts, although they are closely related to each other. The main difference between marketing and selling is that marketing involves understanding and satisfying customer needs and wants, while selling is focused on persuading customers to buy a product or service.
For example, a company that sells smartphones might engage in the following activities:
Marketing:
- Conducting market research to understand customer needs and wants, such as the desire for high-quality camera and long-lasting battery life
- Developing a product that meets those needs and wants, such as a smartphone with a high-quality camera and long-lasting battery life
- Promoting the product to the target audience, such as through social media advertising, email marketing, or content marketing
Selling:
- Engaging with customers who are interested in buying a smartphone
- Highlighting the features and benefits of the smartphone, such as the high-quality camera and long-lasting battery life
- Overcoming any objections or concerns the customer may have about the smartphone
- Closing the sale by persuading the customer to buy the smartphone
In this example, marketing involves understanding and meeting customer needs and wants by developing and promoting a smartphone that meets those needs. Selling involves persuading customers to buy the smartphone by highlighting its features and benefits and addressing any concerns they may have.
HOLISTIC MARKETING
Holistic marketing is a marketing approach that considers the whole business ecosystem in the creation, delivery, and communication of value to customers. It involves integrating various marketing activities and elements, such as product development, pricing, distribution, promotion, and customer service, to create a comprehensive and seamless customer experience.
Example: Tata Group is a conglomerate of companies operating in various industries such as automotive, steel, energy, hospitality, and more. The company has adopted a holistic marketing approach by focusing on creating value for customers through sustainable and socially responsible business practices.
Tata Group’s holistic marketing strategy is its focus on sustainability. The company has set ambitious sustainability goals, such as reducing carbon emissions and increasing the use of renewable energy sources. This focus on sustainability is reflected in its products, such as the Tata Nexon EV, an electric vehicle that promotes sustainable transportation.
Tata Group also focuses on creating a positive impact on society through its social initiatives. Example is the Tata Trusts, a group of philanthropic organizations that work towards improving health, education, and livelihoods in India. This social initiative is reflected in the company’s marketing campaigns, which emphasize the positive impact of its products and services on society.
In conclusion, Tata Group is an excellent example of a brand that has successfully adopted a holistic marketing approach by integrating sustainability and social responsibility into its business practices and marketing strategy.


